Article on Tirzepatide: Latest Guidelines, Uses, and Clinical Evidence in Obesity and Diabetes Management
M3 India Newsdesk May 28, 2025
This article offers a comprehensive overview of Tirzepatide, covering its mechanism of action, dosing guidelines, clinical trial outcomes, potential side effects, and real-world effectiveness, making it a valuable resource for physicians in India.

Tirzepatide is a novel, first-in-class dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, designed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. Its unique mechanism of action offers superior glycemic control, weight loss, and cardiovascular benefits compared to traditional GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Mechanism of Action
Tirzepatide exerts its effects by simultaneously targeting GIP and GLP-1 receptors, leading to:
Enhanced Insulin Secretion
- Both GIP and GLP-1 receptors are present in pancreatic beta cells.
- Tirzepatide stimulates insulin release in response to glucose intake.
Reduced Glucagon Secretion
Suppresses hepatic glucose production, thereby reducing fasting and postprandial glucose levels.
Delayed Gastric Emptying & Appetite Suppression
Leads to prolonged satiety and reduced calorie intake, aiding in significant weight loss.
Improved Beta-Cell Function & Insulin Sensitivity
Studies suggest that tirzepatide preserves pancreatic function, which may help delay disease progression.
Dosing and Administration
Tirzepatide is available as a once-weekly subcutaneous injection. The dosing regimen includes:
- Initiation: 2.5 mg once weekly for 4 weeks (to improve tolerability).
- Escalation: Increase to 5 mg once weekly thereafter.
- If needed, further titration can be done to 10 mg or 15 mg based on glycemic response and tolerability.
Administration Notes
- Can be taken with or without food.
- Rotate injection sites (abdomen, thigh, or upper arm) to prevent lipodystrophy.
- Patients should be monitored for gastrointestinal side effects, particularly during dose escalation.
Clinical Trial Evidence Supporting Tirzepatide
Several pivotal clinical trials have assessed the efficacy and safety of tirzepatide in type 2 diabetes and obesity.
1. SURPASS Trials: Diabetes Efficacy
The SURPASS program included multiple phase 3 trials comparing tirzepatide with placebo, GLP-1 receptor agonists (semaglutide), and basal insulin (degludec, glargine).
SURPASS-1: Evaluated in treatment-naïve patients. Tirzepatide reduced HbA1c by up to 2.1% compared to placebo.
SURPASS-2: Directly compared tirzepatide vs. semaglutide (1 mg). Tirzepatide at 15 mg showed superior HbA1c reduction (-2.4% vs. -1.9%) and greater weight loss (-11.2 kg vs. -6.9 kg).
SURPASS-3 & 4: Showed greater glycemic control compared to insulin degludec and insulin glargine with lower risk of hypoglycemia.
SURPASS-5: Used as an add-on to insulin therapy and significantly improved glycemic outcomes.
2. SURMOUNT Trials: Obesity Management
Tirzepatide is not only a diabetes drug but also a potent weight loss agent. The SURMOUNT trials evaluated its effectiveness for obesity treatment.
SURMOUNT-1: In non-diabetic individuals with obesity, tirzepatide (15 mg) led to an average weight reduction of 22.5% over 72 weeks.
SURMOUNT-2: Similar results in patients with type 2 diabetes, achieving weight loss of up to 15%.
Key Takeaways from Clinical Trials
- Tirzepatide outperforms semaglutide in HbA1c reduction and weight loss.
- Superior to insulin therapy with lower hypoglycemia risk.
- Effective for obesity management even in non-diabetic patients.
Real-World Effectiveness of Tirzepatide
Beyond clinical trials, real-world data suggest that tirzepatide is well-tolerated and highly effective in routine clinical practice.
- A US-based real-world study found that 90% of patients achieved >1% HbA1c reduction within six months of initiation.
- Weight loss outcomes were consistent with clinical trial findings, with 20% weight reduction in many patients.
- Indian patient data is still emerging, but early reports suggest similar efficacy in glycemic and weight management.
Side Effects and Safety Considerations
Like all incretin-based therapies, tirzepatide has some notable side effects:
1. Gastrointestinal Issues (Most Common)
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea
- Appetite suppression, leading to rapid weight loss
- Usually transient and improves after the first few weeks
2. Hypoglycemia Risk
- Higher when combined with sulfonylureas or insulin
- Physicians should adjust insulin doses accordingly
3. Pancreatitis & Thyroid Tumour Risk (Rare, But Serious)
- Contraindicated in patients with a history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or MEN-2 syndrome.
- It should be used cautiously in those with a history of pancreatitis.
Comparison: Tirzepatide vs. Other GLP-1 RA Therapies
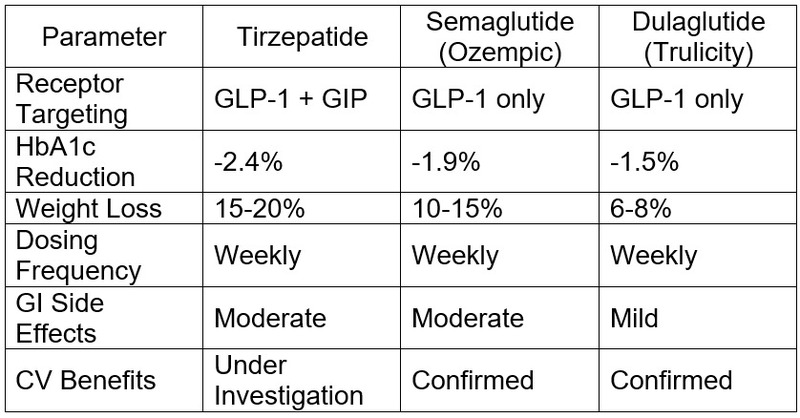
Conclusion & Clinical Implications for Indian Physicians
Tirzepatide represents a transformative advancement in diabetes and obesity management, with unmatched HbA1c reduction and weight loss efficacy. It is particularly beneficial for:
- Patients requiring intensive glucose control without hypoglycemia risk.
- Obese individuals need substantial weight loss along with diabetes treatment.
- Patients who struggle with adherence to daily medications (weekly dosing advantage).
However, cost and availability remain key concerns in the Indian setting. Physicians must weigh clinical benefits against affordability and patient-specific needs.
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr Hitesh Saraogi is a diabetologist, physician and an obesity specialist at Dhanvantari Hospital, Raj Nagar Extension, Ghaziabad.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries