Artice: Adult Vaccination Updates Every Family Doctor Should Know
M3 India Newsdesk May 07, 2025
This article highlights the significance of adult immunisation in preventing vaccine-preventable diseases, details the latest updates in the 2025 vaccination schedule, and guides on identifying, managing, and reporting adverse reactions to ensure vaccine safety.

Adult immunisation is the immunisation of individuals aged 18 years and above, to protect against preventable diseases like tetanus, diphtheria, influenza, COVID-19, etc.
- Many childhood vaccine-preventable diseases develop in adults if they remain unvaccinated during childhood.
- Around 100,000 to 200,000 children are born with defects to mothers who had rubella infection during their pregnancy.
- Around 300,000 new cases of Hepatitis B occur each year, with the carrier state.
- WHO guidelines for adult immunisation focus on a range of vaccines, including COVID-19, pneumococcal, etc., vaccines with recommendations based on age, health status, pregnancy, travelling over the continent, individuals having certain medical conditions, older adults and other risk factors.
- The Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued changes in the 2025 immunisation schedule for children, adolescents, and adults.
- These changes include new and updated recommendations for COVID-19 vaccines, influenza vaccines, meningococcal serogroup B vaccines, pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCV), and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccines.
- These changes are summarised below.
- The 2025 immunisation schedules can be found on the CDC website.
- 2025 Adult Immunisation Schedule Changes:
- The 2025 schedule includes a recommendation to lower the age-based recommendations for pneumococcal vaccination from 65 to 50 years old.
- In addition to the previously recommended 2024-2025 COVID-19 vaccination, the Advisory Committee on Immunisation Practices (ACIP) recommends a second dose of 2024-2025 COVID-19 for adults aged 65 years and older.
- ACIP recommends a second dose of the 2024-2025 COVID-19 vaccine for people ages 6 months to 64 years who are moderately or severely immunocompromised.
- Under shared clinical decision-making, individuals aged 6 months and above who have moderate to severe immunocompromised conditions may receive additional doses (i.e., three or more doses) of the 2024–2025 COVID-19 vaccine.
Why Is Adult Vaccination Important?
- Prevention of disease
- To reduce the risk of disease transmission
- To improve health outcomes
Purpose: To guide health care providers.
Adult Vaccination Schedule (Updated- 2025)
Table 1
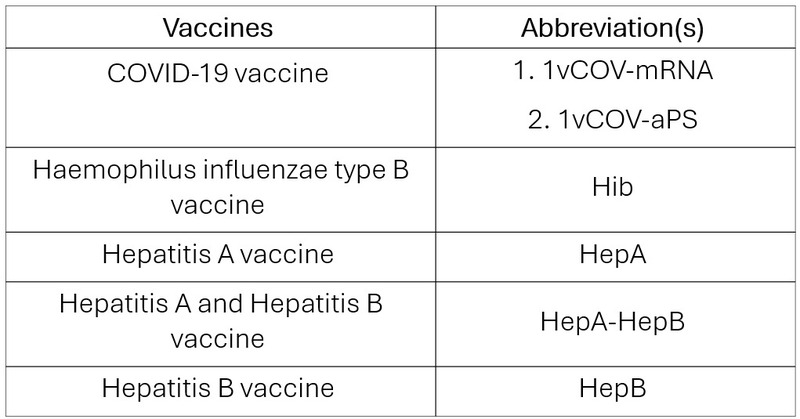
Table 2
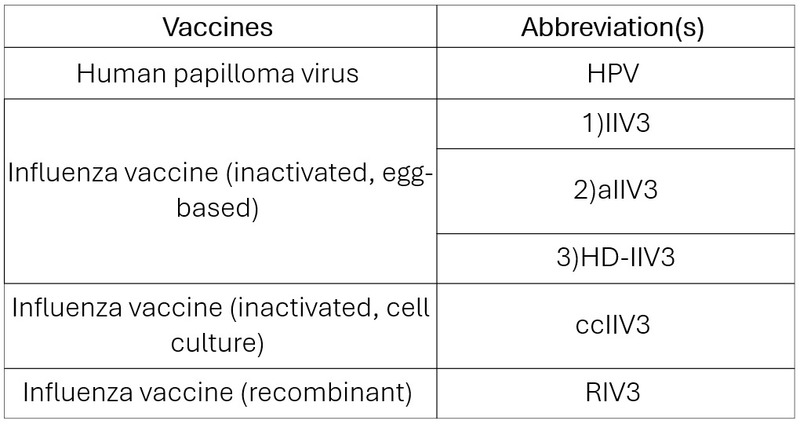
Table 3
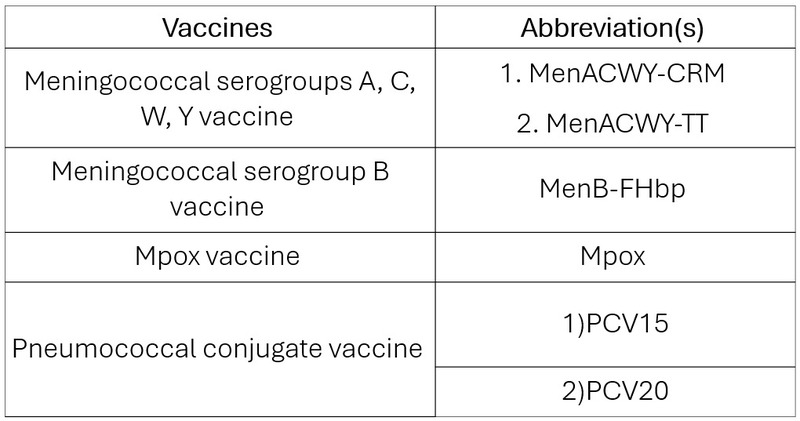
Table 4
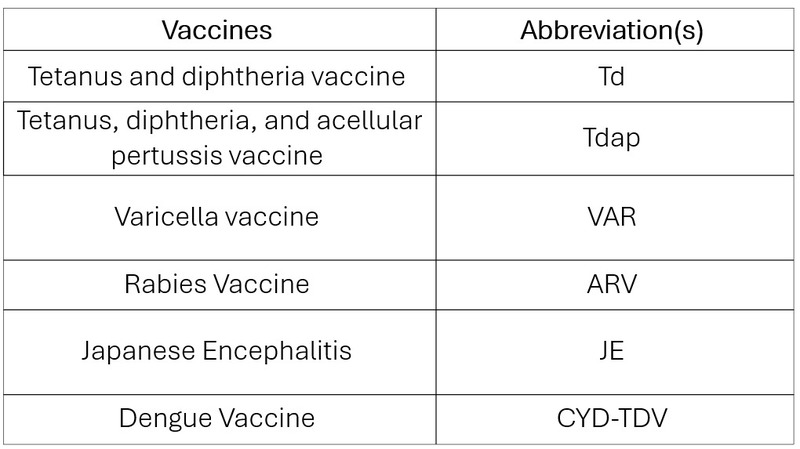
Adverse reactions to adult immunisations
- These are generally mild and temporary.
- These often involve local reactions at the injection site, such as pain, swelling, or redness.
- Some individuals may also experience systemic effects like fever, fatigue, or headache.
- Serious side effects are infrequent.
Common Local Minor Side Effects:
Reactions at the injection site:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Redness
- Itching
These are the most common reactions. These usually resolve within a day or two.
Systemic effects:
- Mild fever
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Joint pain
These are generally short-lived and pose no significant danger.
Rare but Possible Serious Side Effects:
Allergic Reactions: Severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) are extremely rare but can occur.
- Seizures: Seizures following vaccination are also rare.
- Other Serious Events: Rarely, other serious events like temporary low platelet count or Guillain-Barre syndrome may occur, according to the CDC and the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Important Considerations
- Benefits vs. Risks
The advantages of vaccination greatly outweigh the possibility of adverse consequences.
- Seek Medical Advice
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any concerning side effects, such as difficulty breathing, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, or hives.
- Monitoring
Healthcare providers and caregivers monitor for potential side effects after vaccination.
- Vaccine Injury Support Programs
Some countries, like Canada, have programs in place to support individuals who experience serious and permanent injuries after vaccination, according to the BC Centre for Disease Control.
Management of Adverse Reactions to Adult Immunisations
- It typically involves symptom relief and monitoring for serious reactions.
- Common reactions, like soreness or redness at the injection site, can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers and cool compresses.
- Severe reactions, like anaphylaxis, require immediate medical attention, including epinephrine and other emergency procedures.
Common Adverse Reactions and Management
Injection Site Reactions
Soreness, redness, and swelling at the injection site can be managed with:
- Cool compresses
- Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., Tylenol)
- Movement of the limb to encourage lymphatic drainage
Systemic Reactions
Fever, muscle aches, and headache are common and typically subside within a few days.
Allergic Reactions
Itching, hives, or other allergic symptoms can be treated with antihistamines (e.g., Benadryl).
Severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis)
Requires immediate medical attention, including epinephrine injection and emergency medical services.
Anxiety-related Reactions
Can be managed with reassurance and education about vaccine safety, according to a WHO report on adverse events following immunisation (AEFI).
Reporting Adverse Reactions
- All adverse reactions, regardless of severity, should be reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
- Healthcare providers also have a responsibility to report adverse reactions to the appropriate authorities.
Important Considerations
- Vaccines are generally safe and effective. Vaccine-related adverse events are rare and often mild.
- Adverse event reporting is essential for tracking vaccine safety since VAERS data can be used to spot any problems and enhance vaccination safety.
- It's important to distinguish between true adverse events and coincidental events: Some events may be temporally associated with vaccination but not caused by it.
- Anaphylaxis is a rare but serious reaction: It requires immediate medical intervention.
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr Kranti Yadav, M.B.B.S., resident in MD Community Medicine, Government Medical College, Nagpur.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries